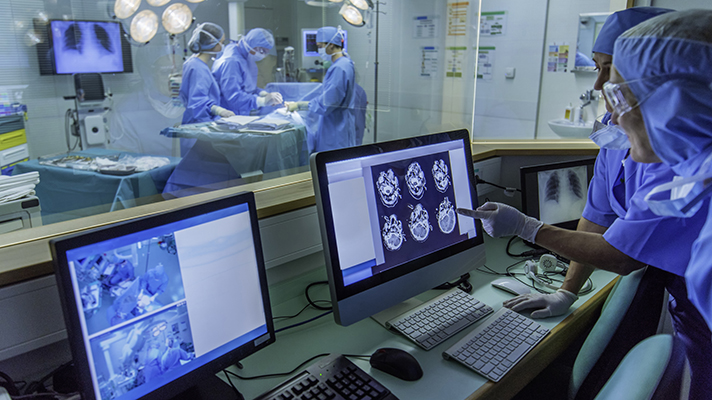
In the realm of healthcare, the physical environment plays a pivotal role in patient outcomes and staff efficiency. Hospitals, once seen as sterile and clinical, have undergone a transformative shift in their design and functionality, largely due to the evolution of installations within their walls. From cutting-edge technology to mindful architectural elements, installations in hospitals have become integral in reshaping the patient experience and improving overall healthcare delivery Etude fluides médicaux.
Technological Innovations:
Advancements in technology have revolutionized healthcare installations. State-of-the-art equipment, such as MRI machines, robotic surgical tools, and remote patient monitoring systems, not only facilitate precise diagnoses and treatments but also streamline medical procedures, minimizing patient discomfort and recovery times. Additionally, the integration of electronic health records (EHRs) has enhanced communication among healthcare providers, ensuring seamless coordination of care and reducing medical errors.
Healing Environments:
Hospitals are increasingly embracing designs aimed at creating healing environments. Natural light, soothing color schemes, and green spaces are now commonplace, promoting a sense of calm and well-being among patients, visitors, and medical staff. Studies have shown that access to nature and views of outdoor spaces can accelerate healing, reduce stress, and even decrease the need for pain medication.
Patient-Centric Amenities:
Installations within hospitals now extend beyond medical equipment to encompass patient-centric amenities. Comfortable waiting areas, private rooms equipped with entertainment options, and adaptable furniture cater to the diverse needs of patients and their families. Furthermore, the inclusion of artwork and interactive installations not only adds aesthetic value but also serves as therapeutic elements, fostering a positive and uplifting atmosphere.
Efficiency and Sustainability:
Efficiency is a cornerstone of modern hospital installations. Automated systems for medication dispensing, smart building technologies regulating temperature and energy usage, and efficient waste management systems contribute to smoother operations and cost-effectiveness. Moreover, an increasing focus on sustainability has led to the incorporation of eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient lighting, and renewable energy sources, aligning healthcare facilities with environmentally conscious practices.
Challenges and Future Trends:
Despite the remarkable progress, challenges persist in implementing new installations. Upgrading existing infrastructure, ensuring interoperability of different technologies, and addressing cybersecurity concerns remain significant hurdles. Moreover, the rapid pace of technological advancements necessitates continuous adaptation and training for healthcare professionals.
Looking ahead, the future of hospital installations appears promising. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applications are poised to transform medical education and patient care, offering immersive experiences for training and therapeutic interventions. Additionally, the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) will continue to expand, connecting medical devices and improving data-driven healthcare delivery.
In conclusion, installations in hospitals have evolved beyond mere functionality, shaping environments that prioritize patient comfort, staff efficiency, and overall well-being.