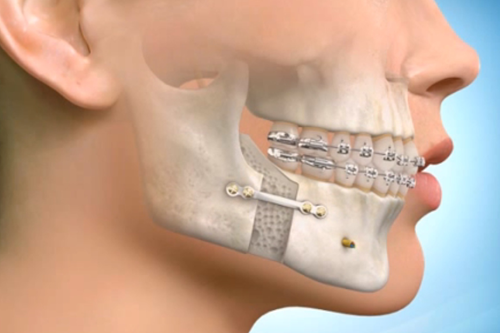
Jaw surgery, also known as orthognathic surgery, is a specialized surgical procedure designed to correct irregularities of the jaw bones and realign the jaws and teeth to improve function and appearance قیمت عمل فک. It can address issues related to chewing, speaking, breathing, and facial balance that cannot be resolved by orthodontics alone.
What is Jaw Surgery?
Jaw surgery involves repositioning the upper jaw (maxilla), lower jaw (mandible), or both to correct structural problems. These issues may be congenital, developmental, or caused by trauma or disease. The goal of the surgery is to improve bite alignment, facial aesthetics, and overall oral health.
Why Is Jaw Surgery Needed?
People may require jaw surgery for a variety of reasons, including:
-
Malocclusion: Severe misalignment of teeth that cannot be fixed with braces alone.
-
Difficulty Chewing or Biting: When the bite is off, it can affect the ability to eat properly.
-
Speech Problems: Jaw misalignment may cause speech impediments.
-
Sleep Apnea: Correcting jaw position can open the airway and reduce obstructive sleep apnea.
-
Facial Imbalance: Uneven jaws can cause asymmetry in the face, affecting appearance and self-esteem.
-
TMJ Disorders: Jaw misalignment can contribute to temporomandibular joint pain and dysfunction.
The Jaw Surgery Process
1. Consultation and Planning:
A multidisciplinary team including an oral and maxillofacial surgeon and orthodontist will evaluate the patient. They use X-rays, 3D imaging, and dental models to plan the surgery precisely.
2. Pre-Surgical Orthodontics:
Braces or other orthodontic devices may be used to align teeth in preparation for surgery, which can take several months.
3. The Surgery:
Performed under general anesthesia, the surgeon makes incisions inside the mouth to minimize visible scarring. The jaw bones are then repositioned and secured with plates and screws.
4. Recovery:
Hospital stays typically last 1–3 days. Swelling, bruising, and discomfort are common during the initial recovery period. Soft foods and limited physical activity are advised while healing takes place over several weeks to months.
5. Post-Surgical Orthodontics:
After healing, further orthodontic treatment may be necessary to refine the bite and alignment.
Risks and Considerations
Like any major surgery, jaw surgery carries risks including infection, nerve injury (which can cause numbness), bleeding, and issues with bone healing. However, when performed by an experienced surgeon and combined with proper orthodontic care, jaw surgery has a high success rate and can dramatically improve quality of life.
Benefits of Jaw Surgery
-
Improved chewing, speaking, and breathing functions
-
Enhanced facial symmetry and appearance
-
Relief from chronic jaw pain and headaches
-
Better oral hygiene due to properly aligned teeth
-
Increased self-confidence and psychological well-being
Conclusion
Jaw surgery is a life-changing procedure for individuals suffering from functional or aesthetic jaw issues. It requires careful planning, expert surgical skill, and collaboration between the patient, surgeon, and orthodontist. For those facing challenges with bite, speech, breathing, or facial balance, jaw surgery offers hope for a healthier, more comfortable, and confident future.